Ais in the field of taxation. AIS "Tax Calculation" Automated Workstation of the Payer (AWS of the Payer) Instructions for installing and configuring the software and components of the "AWS of the Payer" Single-user version Main stages and stages of creation and development
Slide 1. Automated information system “Tax”
represents form of organizational tax management authorities based on new tools and methods of data processing, using formation of new information technologies.
AIS "Tax" allows expand the tasks to be solved, increase the analyticalness, validity and timeliness of decisions made, reduce labor intensity and rationalize the management activities of tax authorities through the use of economic and mathematical methods, computer technology and communications, and streamlining information flows.
Goals functioning of automated information system "Tax":
Increasing the efficiency of the taxation system through efficiency and improving the quality of decisions made.
Improving the efficiency of work and increasing pro-productivity of tax inspectors.
Providing tax inspectorates of all levels with complete and timely information on tax legislation.
Increasing the reliability of data on taxpayer registration and the effectiveness of control over compliance with tax legislation.
Improving the quality and efficiency of accounting.
Receiving data on receipt of taxes and other paymentsto the budget.
Analysis of the dynamics of tax receipts and the possibility of forecasting these dynamics.
Informing administration at various levels about the receipt of taxes and compliance with tax legislation.
Reducing the volume of paper document flow.
Slide 2. Structure of the system of bodies of the State Tax Service of the Russian Federation
Slide 3. Unified centralized system of tax authorities
Control activities primarily involve the State Register of Enterprises and Individuals. The State Register of Enterprises contains official registration information about enterprises (legal entities), and the register of individuals stores information about taxpayers required to declare income, as well as pay certain types of taxes from individuals. The control also includes activities related to documentary inspection of enterprises.
methodological, auditing and legal activities.
The subsystem of methodological, auditing and legal activities provides the ability to work with legislative acts, regulations, decrees and other government documents, as well as with regulatory and methodological documents of the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service. This subsystem carries out processing and analysis of information received from territorial tax inspectorates and concerning the correct application of tax legislation.
analytical activities of territorial inspectorates.
Analytical activities include analysis of the dynamics of tax payments by all categories of taxpayers, forecasting the amount of collection of certain types of taxes, economic and statistical enterprises in the region, identification of enterprises subject to documentary verification, analysis of tax legislation and development of recommendations for its improvement, analysis of the activities of territorial tax inspectorates, etc.
intradepartmental tasks.
Intradepartmental tasks include tasks that ensure the activities of the apparatus of the tax authority at the appropriate level.
Slide 6. Composition of functional subsystems for the local level
· taxpayer registration;
· desk audit;
· maintaining settlement cards (CP) with the budget;
· analysis of financial and economic activities of NP enterprises;
· on-site documentary check;
· maintaining regulatory and legal documentation;
· intradepartmental tasks;
· processing documents of individuals.
NP registration subsystem is associated with the function of timely and complete accounting of taxpayers and payments to the budget. It contains complete information on all taxpayers, both legal entities and individuals.
Slide 7. Cthe remainder of functional subsystems using the example of a municipallevel
registration of enterprises;
desk audit;
maintaining personal cards of enterprises;
analysis of the state of the enterprise;
documentary check.
Slide 8. Workstation
The automated workplace "Administrator" provides:
Protection against unauthorized access to the system;
Separation of system user functions;
Monitoring and restoring the integrity of information stored in the database;
Setting up the program in accordance with the parameters of the tax office and the operating environment;
Adjustment of regulatory and reference information in accordance with the peculiarities of taxation of citizens in this
Region and based on changes in legislation.
AWP "Register of Individuals" provides:
Tax registration;
Removal from tax registration;
Assigning identification numbers to taxpayers;
Preparation of output documents based on user requests.
AWS "Accountant" provides:
Formation of accounting operations;
Entering tax payments;
Maintaining personal accounts of taxpayers;
Generation of output documents for personal accounts and
Statistical reporting.
Slide 9. Supporting subsystems
The supporting part includes informational, technical,software and other types of software specific to anyautomated information system of organizational type.
Information Support includes the entire set of indicators, documents, classifiers, codes, methods of their application in the system the topic of tax authorities, as well as information data sets on computer media used in the automation process solving functional problems.
Technical support represents technicaltechnical means of information processing, the basis of which isThere are computers of varying power and speed, as well as means that allow the transfer of information between different automated workstations, both within tax offices Ghana, and in their interaction with other economicobjects and systems.
Software is a complex of differentfigurative software tools of a general and applied nature,necessary to perform various tasks solved by taxyour organs.
Automated information system of the tax service would belong to the class of large systems. It, like any similar system, is subject to a number of requirements: achieving the goals of creating the system; all elements of this system as in within its framework and with other systems; consistency; decomposition andetc.
Slide 10. Supporting subsystems of the AIS “Tax”
Currently, the technical basis of informatization in the Federal Tax Service is local computer networks based on personal computers such as IBM PC.
The main operating systems are Microsoft products and some such as UNIX. FoxPro, Clipper, MS SQL Server, Access Informix, Oracle are used as database management systems. The main software products operate using “file server” technology, which means there is a local network with several PCs.
Slide 11. Workstation functionality
AWP "Registration of enterprises"
AWP "Desk inspection"
AWS "KRSB NP"
AWP "FHD NP"
AWP allows you to implement the following basic functionality:
- selection of taxpayers for the formation of a plan for on-site inspections based on the analysis of the FCD;
Formation of various documents (decisions, requirements, etc.) used by tax authorities in the process of conducting an audit based on the analysis of the FCD;
Automated calculation of penalties and fines, taking into account the data of the Taxpayers' Investigative Committee in case of detection of violations of tax legislation;
- recording of information on counter inspections carried out;
- automatic generation of various tax authority reporting forms in accordance with orders of the Federal Tax Service;
- formation of financial statements for transferring information to a higher level in accordance with the orders of the Federal Tax Service.
Slide 12. Information support for the automated tax system
Units of information flows can be documents, indicators, details, symbols.
Documentation and contained in theminformation can be divided into the following groups:
1) byplace of compilation:
input (arriving at inspections);
weekends (coming from inspection);
2) by submission deadline:
regulated - documents for which a deadline for execution and submission has been determined;
· unregulated – documents executed upon request.
Slide 13. Unified classification system AIS “Tax”
AIS "Tax" must use the Unified System of Classification and Coding of Information, which is based on the application:
all-Russian classifiers :
· countries of the world (OKSM);
· economic regions (OKER);
· objects of administrative-territorial division and settlements (SOAT);
· public administration bodies (SOOGU);
· branches of the national economy (OKONKH);
· types of economic activities, products and services (OKDP);
· currencies (OKB);
· units of measurement (SOY);
· licensed types of activities (LVD);
· tax returns (TD), etc.
departmental classifiers:
· forms of ownership (FCS);
· organizational and legal forms of economic entities (KOPF);
· budget revenues and expenditures in the Russian Federation (KDRB);
· standard bank accounts (BAC);
· banks (CB);
· tax authorities (NO);
registration authorities, etc.
system classifiers :
· types of documents on registration of categories of land, types of property, types of budget, types of taxes, groups of bankrupts, etc.;
· types of taxable objects (KON);
· tax incentives (TNL);
· types of tax benefits (CTNL);
· penalties (KSHS);
· taxpayer identification numbers (TIN);
· designation systems for state tax inspectorates (SOGNI).
Slide 14. Taxpayer identification number
TIN– an individual is a twelve-digit digital code built according to a positional coding system:
TT NN XXXXXXX SS,
Where TT– code of the territory of the administrative territorial division of Russia;
NN– code of the territorial tax office that carried out the delivery to the taxpayer’s account;
XXXXXXX– the actual serial number of the taxpayer;
SS– symbol (check number).
Slide 15. Information sent by representative authorities to the Federal Tax Service
Bodies of representative power and departments send the following information to the Federal Tax Service:
· orders;
· legislative acts on the introduction of local taxes;
· information about the actual amounts of taxes and other payments received to the budget.
Slide 16.
Law enforcement provide data on vehicles, concealment of income, materials on facts of violations for which criminal liability is provided.
finance provides materials from emission projects, tax deferral data, monthly amounts of taxes and other payments to the budget.
Banks and credit institutions submit payment documents, data on financial and economic transactions of payers for the financial year, on the opening or closing of bank accounts.
Slide 17.
The Federal Tax Service makes submissions for the collection of amounts from taxpayers (excise taxes, VAT), and notifies the Federal Budget on a monthly basis about the receipt of excise taxes and VAT.
Regional bodies The Federal Tax Service provides information corresponding to the rights of access to it, credit and financial authorities, state statistics bodies, and the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
Slide 18. Output information
List of output forms:
· Extract from the payer's personal account (balance on an accrual basis).
· Payer's settlement balance.
· Payer's balance sheet by budget.
· Status of the payer's payments.
· The state of the payer’s payments by budget.
· The state of the payer’s tax payments by budget, etc.
Slide 19. In-machine information support
In-machine information support creates an information environment to meet the various professional needs of users of the taxation system. It includes all types of specially organized information for perception, transmission and processing by technical means. Therefore, information is presented in the form of arrays, databases, and data banks.
Arrays containing other informationare considered permanent (conditionally permanent). In variable masses siwah contains the following information:
Operational control data, ensuring the completeness and timeliness of receipt of taxes, fees, other payments and reporting;
Results of analysis and forecasting of the tax base and the receipt of taxes, fees and other payments;
results of control work of tax authorities;
materials of legal practice of tax authorities, etc.
In permanent arrays contains:
texts of laws, regulations and decrees of the President and Governmentgovernment of the Russian Federation, resolutions of local authorities, otherlegal acts;
texts of orders, instructions and plans of the Federal taxgovernment service;
texts of organizational and methodological documents;
classifiers, reference books and dictionaries used in AIS"Tax";
data from the State Register of Enterprises and accounting datanew taxpayers;
regulatory and reference information of financial, maternaltechnical support, accounting and personnel movement.
Slide 20. Databases
Databases consist of arrays.
Data structuring into database information arrays should be carried out according to the following requirements:
Combining into a single database data that is characterized by a common physical meaning and implements the information technology of one or more interrelated processes of the activities of tax authorities;
Completeness and sufficiency of providing information to officials of tax authorities within the range of data data contained in the input documents;
organizing data into information structures and managementmanaging them through the use of database management systemsdata (DBMS) and ensuring information compatibilitycommunication between different databases;
organizing data in a database, taking into account existing informationnational flows between objects of the AIS “Tax” and within the nationalden authorities;
ensuring information compatibility with data,coming from external levels with which it interactsthis system;
implementation of the principle of consistency and single entry -data used by multiple tasks must bestructured into system-wide structures and supportedby means of software.
Slide 21. Professional databases in tax authorities
The functional and information composition of the database depends on the specifics of each workplace and the qualifications of the specialist. K proprofessional database The tax authorities include databases:
source and reporting data on tax revenues in in terms of sections and paragraphs of the budget classification, budgets, territories, time periods according to regulations standardized reporting forms;
operational data on tax revenues;
letters, precedents, answers, tax proposalslegislation;
derived and integrated data based on reportingforms;
internal documents for various purposes, etc.
Slide 22. Procedure of the tax authorities
The tax office operates in the following order :
Within 24 hours (excluding weekends and holidays) from the moment of receiving reports in electronic form:
· confirms the authenticity of the taxpayer’s electronic signature;
· generates a receipt for receipt of reporting in electronic form (i.e., certifies the received reporting with the electronic signature of the tax authority) and sends it to the taxpayer;
· checks received reports for compliance with the approved format and generates a protocol for incoming reporting control;
· sends the incoming control protocol to the taxpayer.
Slide 23. Protection of information when submitting reports
Data protection when reporting by e-mail, it will be provided with a set of organizational, software and technical measures.
Organizational measures to ensure information security require regulation of the relationships between participants in the exchange of information and strict adherence to the procedure for the exchange of electronic documents when submitting tax returns and reporting forms.
Slide 24. Advantages of the electronic system
Connection to the paperless technology system provides the taxpayer with a number of significant advantages:
· saving time spent on reporting, since there is no need to travel to the tax office and stand in queues;
· expansion of the time frame for submitting reports - files can be sent at any hour (24 hours a day) and any time (7 days a week) until 24 o'clock on the last day of reporting;
· reduction of errors in reporting preparation through means of output control. The taxpayer is given the opportunity to prepare reports in a standard format with control over the correctness of completion and verification of the relevance of the version of the form being filled out;
· guaranteed confirmation of delivery of reports, which has legal force in controversial situations;
· eliminating technical errors (data undergoes input control and is automatically posted to personal accounts) and increasing the efficiency of information processing;
· prompt updating of reporting forms via email.
Slide 25. Consultant Plus system
“Consultant” is knowledge , which is necessary for both tax inspectors and accountants.
Program includes blocks:
· to work with the legislation “Consultant +”, all current changes in acts are made;
· “Consultant + Russian legislation” – all regulations on accounting and taxation
· Consultant “Accountant” version “Prof” – correspondence of accounts, regulatory documents for an accountant, consultations in question-answer mode on the application of legislation.
Slide 26.
A significant place in information supportResearch Institute of AIS "Tax" is occupied by information and reference systems.
For their functioning they create Database:
on legislative and regulatory acts on taxation;
instructional and methodological materials;
on general legal issues.
Functional subsystem databases contain the followingintelligence:
Subsystem “Registration of enterprises” - name of the taxpayer, identification number, location, date of state registration, form of ownership, organizational and legal form, data on founders and authorized capital, etc.;
Subsystem “Desk audit” - results of analysis of accounting and tax reporting of organizations, information about violations of tax legislation identified during desk audits, information about the accounting policy of the taxpayer organization, etc.;
subsystem “Maintaining personal cards of enterprises” - data about tax arrears, about excessively transferred funds,on deferments and installments of payments to the budget, etc.;
Subsystem “Documentary inspection” - number and date of the documentary inspection report, the timing of the inspection, the period for which the inspection was carried out, the nature of the violations identified, the amount of additionally accrued (reduced) taxes and sanctions for violation of tax laws and accrued penalties, etc.
Slide 27. Composition of the Sprinter complex
As part of the Sprinter complex includes:
software module for uploading “1C: Taxpayer”, pre-designated for uploading accounting and tax documentshowl reporting from databases of accounting programs of the family“1C: Enterprise 7.7” or entering these documents manually;
email client program "DiPost", provideexchanging signed digital signatures and encrypted messagescommunication between workstations and electronic serversmail;
control and visualization module "Box Changer", which providesprints output control of reporting files and possiblythe ease of viewing them by taxpayers;
“Referent” program, which provides tax information to the operator about sent reporting files, as well as received operator confirmations and incoming control protocols;
the “Requests” program, which provides the taxpayer withthe possibility of obtaining information upon your requeststatements on the status of settlements with budgets of various levels.
Slide 28.
Program "1C: Taxpayer" represents one ofprograms of the “1C:” family and is supplied in special zated configuration designed to automate the transfer of information both in paper and electronic form to the inspection of the Federal Tax Service, branch of the Pension Fund of Russia, other off-budget social funds, statistical authorities.
The program solves the following problems :
generating a file of information on the income of individuals,intended for transfer to the tax service inspection;
preparation and formation of tax, accounting andstatistical reporting of organizations;
formation of personal data of insured persons and individualindividual information of the insured persons for transfer to the departmentof the Pension Fund of Russia;
maintaining tax cards of individuals receiving incomemoves at the enterprise;
maintaining a list of documents “Certificate of income of an individual”faces";
generation of a “Certificate of Income of an Individual” for yougiving to individuals.
Slide 29.
The state of the AIS “Tax” as a whole can be characterized as follows :
· information technologies in the Russian Federal Tax Service are developing towards the creation of a unified system based on the relationship of work processes and information services using the best practices of foreign countries;
· prototypes of basic information services were created to support tax administration workflows;
· unification and standardization of tax administration work processes contributes to the stability of the information system of the Federal Service of the Russian Federation;
· clear and close partnership between methodological departments and IT services - the efficiency of the tax system;
· the telecommunications system is an important link in the tax authorities’ system;
· organization of information security is based on technological solutions and recommendations of the Special Communications Service and the State Technical Commission;
· as part of the implementation of the 2nd Project for the modernization of tax authorities of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation:
– work continued on the development of such subsystems of the automated information system for interdistrict inspectorates for centralized data processing, such as: the system for the preparation and exchange of tax information (SPONI), the system for processing tax information (SONI); Work has begun on creating a tax inspection service subsystem (SOIMNS).
– in many territorial inspectorates of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation, a local-level software package (“client-server”) is being implemented.
Slide 30.

Slide 31.
Slide 32.

Slide 33.

Slide 34.
Slide 35.
Questions for self-control
1.What is the hierarchical structure of the system of tax authorities of the Russian Federation?
2. Describe the functions performed by lower-level tax authorities.
3.What are the goals of the functioning of the AIS “Tax”?
4.Describe the structure of the AIS “Tax”. List the composition of the supporting part.
5.What is the composition of the functional part of the AIS “Tax”?
6. Show, using the example of tax inspectorates and districts, the order of implementation of the tasks of the functional subsystems of the AIS “Tax”.
7.Give me the workstation. List the composition of automated workplaces organized in tax inspectorates.
8. Composition of off-machine support for AIS “Tax”?
9.What classifiers are used in the tax system?
10. List the composition of the in-machine software of the AIS “Tax”.
(10
ratings, average: 4,90
out of 5)

The AIS Tax-3 program is constantly changing, and new functions are being added to it. Very soon the tax service will normalize its work and it will be much easier to carry out audits, as well as justify the reasons for the audits. Such a system will soon become a single database for all taxpayers in the country. Also, such a database will include not only taxes, but also data from banking organizations and law enforcement agencies.
Preparations for such changes began many years ago. This is evidenced by the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated October 20, 2016 No. ЗН-18-1/1103@. It is planned to put the entire system into operation in 2019 without any technical errors. All aspects of business will now be reflected by tax inspectors. If a company or citizen is dishonest in its activities, the software will automatically notify the tax authority about this.
At the moment, the system is running in test mode, however, its performance is very serious. Online, inspectors can find out all the information on companies and individual entrepreneurs, even if they are registered in another region.
The tax authority can now track information:
About each director of the company.
About all the founders of the organization.
About the company's divisions that are separate.
About individuals who are related to taxes.
All documentation about registrations.
Availability of bank accounts.
Balance of funds in accounts with banking organizations.
About transactions that were made with bank accounts.
About accounting reports.
About tax reports.
Books of purchases and sales not only of the company, but also of all its suppliers and contractors.
About the calculation of tax payments.
About tax deductions.
The presence of risky situations that have already been confirmed by the tax service.
System failures are rare. Therefore, most likely there will be no errors in it. For example, it may happen that the program gets confused in sets of tax identification numbers or produces an incorrect list of tax objects for individuals. It has already happened that the system reacted to a company that allegedly had risks due to the interrogation of the director; he refused to contact one of the companies. But it turned out that the tax inspectorate simply interrogated the namesake of the manager.
The fact is that the director, or his refusal to contact the company, may become the very first risk of receiving tax demands and claims. The tax authority refuses to discuss methods for assigning risks using the program. Because the Federal Tax Service does not want to encounter in the future new schemes of businessmen to defraud such a program.
One thing is known that the ASK VAT-2 program displays all risks using an indicator. In this way, inspectors can track if a company lights up red, which means it’s worth going deeper into checking the documentation. If it is green, then most likely the company does not have any risks. This is stated in the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated 06/03/2016 No. ED-4-15/9933@ “On the assessment of RMS risk indicators.”
AUTOMATED INFORMATION SYSTEM “TAX”
To implement all these functions in the management system of the State Tax Service of the Russian Federation, the automated information system “Tax” was created. The software is the property of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation and is provided to inspections through the Federal Tax Service Fund of Algorithms and Programs (FAP) free of charge.
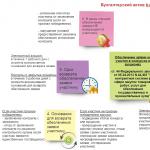
The automated information system “Tax” is a form of organizational management of the State Tax Service bodies based on new tools and methods of data processing, and the use of new information technologies. AN S "Tax" allows you to reduce labor intensity and rationalize the management activities of tax authorities through the use of economic and mathematical methods, computer technology and communications, and streamlining information flows. We can say that AN S “Tax” is an information model of tax authorities.
Rice. 4.1.
The goals of the automated information system “Tax” can be formulated as follows:
- - increasing the efficiency of the taxation system through efficiency and improving the quality of decisions made;
- - improving the efficiency of work and increasing the productivity of tax inspectors;
- - providing tax inspectorates of all levels with complete and timely information on tax legislation;
- - increasing the reliability of data on taxpayer registration and the effectiveness of control over compliance with tax legislation;
- - improving the quality and efficiency of accounting;
- - obtaining data on the receipt of taxes and other payments to the budget;
- - analysis of the dynamics of tax receipts and the possibility of forecasting these dynamics;
- - informing administration at various levels about the receipt of taxes and compliance with tax legislation;
- - reduction of paper document flow.

Rice. 4.2.
The architecture of the AIS “Tax” has its own characteristics, which are determined by the following list of requirements:
- - the structure of the AIS must correspond to the structure of the tax system;
- - the content of the AIS must correspond to the subject area of the tax system (tasks, documents);
- - the information processing system in AIS is implemented on the basis of network information technology in tax services;
- - when developing information, software and technical support for AIS, it is necessary to take into account the unity of standards, terminology, and unification of design methods.
Functionally, the AIS “Tax” consists of application software systems, including:
- - complex “Taxation, ensuring the collection of taxes and other payments, tax reporting”;
- - complex “Ensuring and monitoring compliance with tax legislation”.
The complex “Taxation, ensuring the collection of taxes and other payments, tax reporting” is intended for:
- - accounting of taxpayers;
- - operational accounting in the field of taxation;
- - desk audits of tax calculations;
- - maintaining tax statistics and reporting;
- - accounting and control of bank accounts;
- - accounting of cash registers;
- - processing information on foreign economic activities of taxpayers according to the State Customs Committee of the Russian Federation.
The “Ensuring and monitoring compliance with tax legislation” complex allows you to solve:
- - drawing up, analyzing and adjusting schedules for conducting documentary checks and their types;
- - collection and analysis of information necessary for conducting documentary checks from other subsystems of the AIS “Tax” using the query system;
- - collection and analysis of information necessary for conducting documentary checks from external automated systems;
- - storage of the amounts and types of identified amounts (concealment, overpayments, fines, etc.), acts based on the results of documentary checks, proposals for acts, log books, inspections and offenses;
- - receipt and transfer to the operational accounting subsystem of the results of documentary checks - amounts of hidden taxes, additional charges, overpayments, penalties and interest;
- - modification of input and output interface and reporting forms when instructions for obtaining consolidated official reporting documents change;
- - accounting of administrative measures imposed on taxpayers - individuals.
The AIS "Tax" implements inter-level (local - regional - federal) information interaction based on the creation of integrated distributed databases. According to special regulations at the federal level, data from the State Register of Taxpayers, tax statistical reporting, business and departmental correspondence are collected through communication channels and summarized. Directive instructions, methodological and normative reference materials, certified software and modifications to it are received from the Federal Tax Service via electronic channels.
For the full use of information technology tools in the daily activities of the Federal Tax Service, it is necessary to obtain information from almost all databases currently available in the information environment of tax authorities. In addition, additional databases with information coming from external organizations should be created, or permanent information links with them should be implemented.
The automated information system “Tax” has the following main databases.
- - state register of taxpayers - an integrated multi-level database, including identification, statistical, accounting and other characteristics;
- - an integrated multi-level database of bank accounts of taxpayers, containing information about various types of bank accounts, about the banks in which the accounts are opened;
- - a comprehensive database of personal accounts of each taxpayer - information on the composition of taxes paid, tax benefits, accrued and paid amounts of taxes, fines, penalties, existing arrears, overpayments, refunds from the budget, granted deferrals of tax amounts;
- - a database of mandatory reporting documents that are defined by tax legislation to indicate the tax base and calculate taxes themselves;
- - a database of control (documentary) audits of taxpayers, containing information about schedules for conducting documentary audits, acts based on their results, proposals for acts, tax violations, protocols, resolutions, claims to the judiciary;
- - a regulatory database containing regulatory and reference information - all-Russian classifiers and reference books, tax regulations;
- - a database with additional information about taxpayers.
The third level is characterized by its own composition of functional subsystems:
- - registration of enterprises;
- - desk audit;
- - maintaining personal cards of enterprises;
- - analysis of the state of the enterprise;
- - documentary check;
- - maintaining regulatory documentation;
- - intradepartmental tasks;
- - processing of documents of individuals.
The enterprise registration subsystem is associated with the function of timely and complete accounting of taxpayers and payments to the budget. It contains complete information on all taxpayers, both legal entities and individuals.
When registering or re-registering any enterprise, all initial data about it must be recorded and entered into the State Register. Tax authorities use them as basic information for each taxpayer, so they must be entered into a computer and used in other subsystems, for example, in desk audits or when maintaining personal cards of enterprises.
The desk audit subsystem is associated with such functions as monitoring the accuracy and timeliness of taxpayers submitting accounting reports and tax calculations, reports and declarations, calculation and payment of taxes and other payments to the budget. The subsystem is necessary to automate procedures related to the acceptance of financial statements of enterprises, as well as tax calculations. The tasks of this subsystem include checking calculations, linking reporting forms and tax calculations, issuing recommendations for conducting documentary checks.
The subsystem has internal connections with other subsystems, such as registration of enterprises, maintaining personal cards of enterprises, documentary verification, etc.
The subsystem for maintaining personal cards of enterprises is associated with obtaining data on tax receipts in the context of taxpayers and types of taxes, monitoring the timeliness of payment of taxes to the budget, calculating penalties, calculating balances according to calculations, issuing any certificates of arrears and overpayments for enterprises, etc. The subsystem for analyzing the state of enterprises is interconnected with the subsystems for registering enterprises, as well as desk and documentary checks, because the analysis is carried out on the basis of data obtained both during the registration of enterprises and during a desk audit.
As a result of the analysis, a list of enterprises is determined that have violations in the procedure and deadlines for submitting basic documents necessary to obtain data on taxes and other payments to the budget and their payment. Based on this, a list of enterprises subject to documentary verification is formed.
The documentary verification subsystem refers to the control activity of tax authorities. It is one of the most important functional subsystems, because ensures the performance not only of functions that are characteristic of other functional subsystems of the AIS “Tax”, but also has its own additional tasks, which include monitoring the correct implementation and execution by taxpayers of legislative and other administrative documents, identifying violations of this legislation, determining sanctions for violations etc. This subsystem is connected to almost all other functional subsystems of the AIS “Tax”.
The subsystem for maintaining regulatory and legal documentation provides the ability to work with legislative acts, regulations, decrees, orders and other documents issued by the Government of the Russian Federation, the State Tax Service and other departments. Based on the information of this subsystem, the work of all tax authorities is built, and, accordingly, the functioning of the remaining subsystems.
The subsystem of intradepartmental tasks includes tasks related to office work, personnel, accounting, logistics and other activities of the tax authority as a separate organizational structure.
The subsystem for processing documents of individuals can be separated into a separate part of the functional support, because it must exercise control and management of information on the main types of taxes collected from individuals, provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
It includes most of the tasks solved in all functional subsystems related to the processing of information on legal entities. This subsystem operates on the basis of the application of legislative acts that allow the tax service to monitor the correctness of calculation of income tax, personal property tax, land tax and other taxes. The subsystem calculates tax amounts, maintains personal accounts, prints notices about the amounts of accrued taxes, and prepares various accounting reports.
Let's consider the procedure for implementing the tasks of the main subsystems of the functional part of the AIS “Tax”.
Information processing begins with accounting and registration of taxpayers, which is carried out by the legal service of the tax inspectorate. This service receives from the taxpayer all the necessary registration documents, on the basis of which a database is created containing all information about the taxpayer and assigns the taxpayer a unique registration number. An “electronic folder” is created for the taxpayer. The information contained in it is used by all other structural divisions of the tax inspectorate.
First of all, the consumer of this information is the “Desk Check” subsystem. To solve the problems of a desk audit, the tax inspector service collects reporting documents from taxpayers within the time limits established by law.
Thus, the main documents are the balance sheet of the enterprise, the profit and loss statement, appendices to the balance sheet, calculations for income tax, VAT, corporate property tax and other tax calculations.
A desk audit consists of determining the correctness of filling out financial statements, calculating tax amounts, and accurately filling out forms. To do this, the reporting data submitted by the taxpayer is entered into the computer and the taxpayer’s “electronic folder” is replenished with new information that allows tracking the main indicators of the results of the financial and economic activities of the enterprise in different periods.
Solving desk audit problems involves using not only data generated in the “Registration of Enterprises” subsystem, but also regulatory and reference information on organizational and legal forms, tax rates, payment terms, various tax benefits and other information created in the “Maintenance” subsystem regulatory documentation".
The use of computer technology allows you to monitor the dynamics of the development of an enterprise, its compliance with tax legislation, identify violations of this legislation, charge payments to the budget and create a list of enterprises for documentary verification.
Ultimately, the information generated in this subsystem serves as the basis for solving the problems of other functional subsystems related to the processing of data on taxpayers - legal entities. First of all, this concerns documentary checks. Documentary checks are carried out by tax inspection services according to regulations. The purpose of the documentary check is to identify the correctness and reliability of the organization and maintenance of accounting at enterprises, the timeliness and completeness of payment of taxes and other payments to the budget, as well as the correct application of existing benefits.
The audit is carried out at the location of taxpayer enterprises. It involves reviewing all necessary documentation of the enterprise in order to achieve the goals of the documentary audit. The use of computer technology to solve the problems of a documentary audit makes it possible to draw up an audit report, which sets out all violations of tax legislation and the procedure for organizing and maintaining accounting at the audited enterprise, if they occur, and to accrue fines and penalties in accordance with the qualifications of violations. To do this, it should be possible to access databases of such subsystems as “Registration of enterprises”, “Desk audit”, “Maintaining legal documentation”. The information generated in the “Documentary Inspection” subsystem is used by the “Maintaining Enterprise Personal Cards” subsystem to record arrears or overpayments of taxes, as well as reflect data on the sanctions applied based on the inspection report.
Using a computer in the subsystem “Maintaining personal cards of enterprises”, the balance of settlements between the enterprise and the budget for each tax is revealed. Data for each taxpayer enterprise on accrued amounts of taxes comes from the subsystems of desk and documentary audits. Banks receive information about taxes paid and money credited to the appropriate budget account. Comparison of accrued and paid amounts for specific taxes and periods allows you to determine the balance of calculations. As a result, the amounts of arrears or overpayments for all taxes and tax payments to the budget are determined.
The automated information system “Tax 2 Moscow” is designed to automate tax administration processes carried out by tax authorities at the regional and local levels. The system meets all the necessary requirements set by the Federal Tax Service for software, hardware and information support, and is also certified within the framework of the GOST R certification system of the State Standard of Russia.
AIS “Tax 2 Moscow” is a unique information system designed specifically for functioning in the conditions of the largest regions. The high concentration of capital and business activity, and, as a consequence, a high share of revenues to budgets at various levels, require special attention to the automation of tax administration processes. AIS “Tax 2 Moscow” was initially designed and created taking into account the following factors:
- Large volumes of information to be entered and processed.
- A large number of system users.
- Increased requirements for reliability and fault tolerance.
- Developed telecommunications infrastructure.
- Does not impose high requirements on the level of user training in the field of information technology to work in the system, its maintenance and support.
Distinctive features
- AIS "Tax 2 Moscow" designed as unified distributed information system, covering the Department of the Federal Tax Service for Moscow, territorial and interdistrict inspections. AIS "Tax 2 Moscow" at the local level, AIS "Tax 2 Moscow" at the regional level, as well as software systems for the Data Processing Center and the Unified Registration Center.
- Centralized maintenance of regulatory and reference information, document templates and other configuration information at the regional level. At the local level, a minimum set of inspection-specific settings is left.
- System activity- the user does not need to constantly keep in memory a lot of information about taxpayers and the timing of tax measures - the system itself will “tell” the user that he is working with a taxpayer who is a participant in a tax evasion scheme, will issue recommendations for carrying out the necessary measures to eliminate arrears, and will warn about the approaching deadline issuing a demand for payment of tax, forming a decision on the collection of funds and other possible actions.
- Friendly interface. One of the main principles laid down in the Tax 2 Moscow AIS is ease of operation for the end user and an intuitive understanding of the user interface. For this purpose, the system functions are implemented in the form of modes or scenarios that determine the typical sequence of user actions. Electronic forms of documents and tax returns closely replicate approved paper forms.
- All components of the AIS “Tax 2 Moscow” are implemented in a single architecture, are interconnected at the level of the information model and at the level of software interfaces, subject to uniform rules of administration and technical support.
- Performance and Reliability are ensured by the use of a three-tier application architecture, which ensures the possibility of simultaneous operation of a large number of users and allows scaling the system by connecting additional application servers as the load increases and choosing Oracle DBMS as the database management system.
Local functions
AIS "Tax 2 Moscow" automates all the main functions of tax administration: from registration and accounting of taxpayers to on-site audits and the generation of statistical reporting, both for legal entities and individuals.
Regional level functions
A unique block of control and analytical functions implemented at the regional level (Taxpayer File, Federal Tax Service File, Analysis of data on the mobilization of budget revenues, Monitoring of main business processes) allows you to receive current information in real time for the Department as a whole, in the context of inspections or for a specific to the taxpayer. These capabilities are provided by subsystems at the local level, which specifically include functions for promptly submitting the necessary information to the regional level.
Escort service
- For effective support and support, a specialized service has been organized, a support website has been developed and is actively operating, through which interaction between users, methodologists and system developers occurs, the completeness and timeliness of answers to user questions and the processing of proposals for system development are monitored. Information about emergency situations occurring in the system is sent to the website automatically.
- Automated controls over the deployment of AIS “Tax 2 Moscow” ensure complete identity of the system in all inspections at the local level, which significantly simplifies the IT administration of the system and allows you to switch to system support by a centralized IT service from the regional level.
- Despite the fact that the Oracle DBMS is used as a database management system, IT service employees performing the functions of administering and maintaining the AIS “Tax 2 Moscow” do not require in-depth knowledge of the DBMS itself, since all actions for servicing the system are clearly regulated by the relevant instructions, which are updated with each new version of the software product.
Modern technologies
The open architecture and the use of the most modern technologies in the development make it possible to quickly implement such interesting and promising solutions as information interaction with taxpayers via communication channels in real access mode (on-line), including access to personal account data and submission of reports via the Internet. Using the principles of a single information space and mechanisms for remote access to data laid down in the AIS “Tax 2 Moscow”, solutions were quickly implemented to track participants in tax evasion “schemes” and to automate the VAT Refund Commission operating in the Federal Tax Service in Moscow.
About the developers
Teams of specialists from the State Scientific Research Center of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, T.I. Systems, OVIONT INFORM and AMM-TaxPro, who have extensive experience working on projects with federal and regional government departments, took part in the development and development of the system. The work of the teams is organized in accordance with the requirements of GOST ISO 9001-2001, which is confirmed by the Certificate of Conformity.
Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation
THE FEDERAL TAX SERVICE
ORDER
On approval of the Regulations on the automated information system of the Federal Tax Service (AIS "Tax-3")
In order to systematize the main approaches to the creation, development, maintenance and use of the automated information system of the Federal Tax Service
I order:
1. Approve the Regulations on the automated information system of the Federal Tax Service (AIS "Tax-3") (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations) in accordance with the appendix to this order.
2. The heads of structural divisions of the central apparatus of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, heads of departments of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, heads of interregional inspectorates of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, general directors of organizations subordinate to the Federal Tax Service of Russia, will in the future be guided by the requirements of the Regulations.
Supervisor
Federal Tax Service
M.V. Mishustin
Regulations on the automated information system of the Federal Tax Service (AIS "Tax-3")
APPROVED
by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia
from "__" _______ 2016 N _______
I. General provisions
1. These Regulations define the purpose and tasks of the automated information system of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as AIS "Tax-3"), the structure and main functions of AIS "Tax-3", users of AIS "Tax-3", the procedure for providing access to AIS "Tax-3", legal status of software and hardware of AIS "Tax-3", rules for information interaction of AIS "Tax-3" with other information systems.
II. Purpose and tasks of AIS "Tax-3"
2. AIS "Tax-3" is a unified information system of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, providing automation of the activities of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for all functions performed, determined by the Regulations on the Federal Tax Service, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 30, 2004 N 506 (in the current version, hereinafter - Regulations on the Federal Tax Service of Russia), including the reception, processing, provision of data and analysis of information, the formation of information resources of tax authorities, statistical data, information necessary to support management decisions in the sphere of authority of the Federal Tax Service of Russia and the provision of information to external consumers.
3. AIS "Tax-3" was created with the aim of increasing the efficiency of implementing powers and solving problems defined in the Regulations on the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
a) ensuring the “openness” of tax authorities for the taxpayer, by simplifying the procedures for his interaction with the Federal Tax Service of Russia and converting them into electronic form;
b) creation of a unified information array and connection of tax authorities to new external sources of information;
c) guaranteed compliance with regulatory tax administration procedures, quality and timing of their implementation;
d) reducing the current costs of tax administration, primarily through the creation and implementation of an electronic system for mass processing of information received by the tax authorities;
e) improving procedures for information interaction with state authorities and local governments;
f) ensuring control over the tax activities of the taxpayer by creating a single and reliable resource containing all the information on a specific taxpayer (“taxpayer’s “dossier”), including information that allows timely identification of signs of tax evasion;
g) ensuring automated monitoring of the activities of the Federal Tax Service by the management of tax authorities;
h) improving the quality of control work, including through the integrated use of the created single information resource and connecting tax authorities to new external sources of information;
i) improving the quality of decision-making, analysis and forecasting through the creation of analytical tools that allow analysis and forecasting of tax revenues taking into account macroeconomic indicators and external factors.
Additional tasks include:
a) reducing the labor costs of tax authorities for collecting, entering, processing and monitoring tax reporting forms;
b) reducing the labor costs of tax authorities to ensure interdepartmental exchange of information, freeing tax authorities from the functions of receiving, processing and sorting data coming from other departments;
c) reducing the labor costs of tax authorities to carry out calculations, including the calculation of taxes and control of tax reporting;
d) transition from quantitative to qualitative analysis of taxes and the tax base, including as part of improving control work;
e) ensuring the possibility of internal audit of the work results of employees of territorial tax authorities and the central office of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
III. Users of AIS "Tax-3"
5. Users of information resources of AIS "Tax-3" are:
a) the central office of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, territorial tax authorities - departments of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, interregional inspectorates of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, inspections of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for districts, districts in cities, cities without district division, inspections of the Federal Tax Service of Russia at the interdistrict level (hereinafter referred to as tax authorities) ;
b) organizations subordinate to the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
Users of information and information from the AIS "Tax-3" are also federal executive authorities, executive authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local governments and taxpayers (in accordance with current agreements, hereinafter referred to as external users).
IV. Basic principles of construction and functions of AIS "Tax-3"
6. The basic principles of constructing the AIS "Tax-3" are:
a) systematization of the collection, storage and use of information when tax authorities exercise the powers assigned to the Federal Tax Service of Russia;
b) provision of information to external users, as well as the exclusion of repeated requests for information contained in the AIS "Tax-3" from the source of information;
c) the relevance and reliability of the information contained in the AIS "Tax-3";
d) adaptability of the composition of information contained in the AIS "Tax-3" to the changing requirements of users and legislation;
e) openness to integration of AIS "Tax-3" with existing and created state and other information resources, departmental and interdepartmental information systems based on a unified system of directories, classifiers and unified standards of information interaction;
f) the unity of terms used in the AIS "Tax-3", normative and reference information, a system of indicators and regulatory reporting;
g) unity of standards, technologies, formats of all elements of the AIS "Tax-3";
h) compliance with information security requirements;
i) openness and accessibility of information contained in the AIS "Tax-3", with the exception of restricted access information.
7. AIS "Tax-3" provides automation of the activities of the Federal Tax Service of Russia according to the functions performed, determined by the Regulations on the Federal Tax Service of Russia, and is represented by components that perform the functions of:
a) collection, systematization, processing, storage of data and provision of information contained in the AIS "Tax-3", implementation of format-logical control of data, identification of inconsistencies and discrepancies in data received from various sources, and harmonization of information contained in the AIS " Tax-3", as well as to ensure integration with information systems of federal executive authorities, executive authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments, the information resources of which are intended for making management decisions, and information resources of other information systems, the need for integration with which is determined functional requirements;
b) external interaction with taxpayers, individuals and legal entities (in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and existing agreements);
c) centralized maintenance and provision of access to registers, directories and classifiers used in the AIS "Tax-3", and the generation of data necessary to perform the functions assigned to the tax authorities and make management decisions;
d) comparison and analysis of information contained in the AIS "Tax-3", as well as providing information and analytical support for making management decisions, including using tools for monitoring, evaluating and controlling information contained in the information resources of tax authorities;
e) ensuring free access to regulatory, statistical and analytical information in the field of public administration in terms of the powers assigned to the Federal Tax Service of Russia, through the portal (website) of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, which is a public information resource.
V. Component composition of AIS "Nalog-3"
8. The main components of the AIS "Tax-3" include:
a) centralized components located at the federal level (segments for operational and analytical work);
b) decentralized components.
VI. External information interaction of AIS "Tax-3"
9. Information interaction between the AIS "Tax-3" and other information systems is carried out at the federal, regional and local levels.
The information interaction of the AIS "Tax-3" and other information systems in these Regulations means a set of information processes aimed at obtaining and using the AIS "Tax-3" information contained in other information systems, and the use of such information in electronic form in the AIS " Tax-3", as well as for the receipt and use by users of other information systems of information contained in the AIS "Tax-3".
10. Information interaction between AIS "Tax-3" and other information systems is carried out using technical and software tools of AIS "Tax-3" based on the exchange of electronic documents (information requests and information messages) sent by participants in information interaction.
When organizing the interaction of the AIS "Tax-3" and other information systems, the infrastructure is used to ensure the information and technological interaction of information systems used to provide state and municipal services and perform state and municipal functions in electronic form.
11. Information interaction of AIS "Tax-3" with other information systems is carried out with the following requirements:
a) protection of transmitted information from unauthorized access, destruction, modification, blocking, copying, distribution, and other unlawful actions from the moment of transfer of this information from another information system until its receipt in the AIS "Tax-3";
b) organizing access to information in cases and in the manner provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
c) recording the date, time and participants of all actions and operations carried out within the framework of information interaction, as well as the ability to provide information that allows one to restore the history of information interaction;
d) immediately informing the owners of information systems interacting with the AIS "Tax-3" about failures and irregularities in the operation of the AIS "Tax-3" and other information systems, which may lead to a violation of the timing and quality of providing and (or) receiving information, and also about violation of information security requirements defined by these Regulations;
e) immediate implementation of measures to eliminate identified failures and disruptions in the functioning of the AIS "Tax-3" and cases of violation of information security requirements;
f) confirmation of the reliability and relevance of information transmitted from the AIS "Tax-3" to other information systems, and if the information is found to be unreliable - ensuring its updating and informing interested participants in information interaction about this change and about cases of revealing unreliable information;
g) signing using an electronic signature of information transmitted to another information system.
12. Technological means of AIS "Tax-3" ensure the unity of regulatory and reference information contained in AIS "Tax-3", including reference books and classifiers used by AIS "Tax-3".
The list of directories and classifiers used in the AIS "Tax-3", as well as the procedure for their formation and maintenance in the AIS "Tax-3" are established by the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
The placement and maintenance of directories and classifiers used within the framework of the AIS "Tax-3" is carried out in specialized means of maintaining normative and reference information.
13. Hardware and software tools of the AIS "Tax-3" provide technical protection of information contained in the AIS "Tax-3" by means of:
b) maintaining electronic logs of transactions performed using hardware and software that allow for recording of all actions to place, change and delete information, record the exact time, content of changes and information about the user who made the changes;
c) the use of means of ensuring uninterruptible power supply, backup, recovery and duplication (mirroring) of information, ensuring the possibility of recovering information;
d) protecting information from unauthorized copying, distribution, destruction, modification and blocking of access to it, as well as from other illegal actions;
e) saving copies of information and electronic logs of transactions in accordance with the backup regulations established by the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
14. Hardware and software tools of the AIS "Tax-3" in terms of protecting the information contained in the AIS "Tax-3" correspond to:
a) Federal Law of July 27, 2006 N 149-FZ “On information, information technologies and information protection”;
b) Federal Law of July 27, 2006 N 152-FZ “On Personal Data”;
c) Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 1, 2012 N 1119 “On approval of the Requirements for the protection of personal data during their processing in personal data information systems” (hereinafter referred to as Decree N 1119 dated November 1, 2012);
d) Order of the FSTEC of Russia dated 02/11/2013 N 17 “On approval of the Requirements for the protection of information that does not constitute a state secret contained in state information systems” (hereinafter referred to as FSTEC Order N 17 of 02/11/2013);
e) Order of the FSTEC of Russia dated February 18, 2013 N 21 “On approval of the composition and content of organizational and technical measures to ensure the security of personal data during their processing in personal data information systems”;
f) regulatory and methodological documents of the FSTEC of Russia on ensuring information security in key information infrastructure systems;
g) technical requirements for the interaction of information systems in a unified system of interdepartmental electronic interaction, approved by the Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications of the Russian Federation.
15. Hardware and software of the AIS "Nalog-3" provide:
a) Round-the-clock (except for the time for routine maintenance) availability of the AIS "Tax-3" for receiving and using (including in the form of open data) information posted in the AIS "Tax-3";
c) conducting regular monitoring of the performance and availability of the functions of the AIS "Tax-3";
d) the ability for users of the AIS "Tax-3" to search and receive text information and aggregated statistical data;
e) division of automated functions of the AIS "Tax-3" into those requiring interactive interaction of users with the system and those not requiring such interaction, performed by the "tax machine";
f) automated verification of taxpayer data according to the data contained in the AIS "Tax-3" and immediate notification of the inspector about possible violations of the law;
g) the ability to increase functional and technological capabilities in terms of the number and volume of tasks to be solved, the types and number of interacting information systems, adaptation to various changes;
h) the possibility of automated assessment of labor costs of employees of tax authorities and employees of organizations subordinate to the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the implementation of technological processes in the AIS "Tax-3".
16. Linguistic means of the AIS "Tax-3" provide access to the subjects of the system, users of the AIS "Tax-3" to the information contained in the AIS "Tax-3" in Russian.
17. Additional (special) requirements for technological, technical, software and linguistic means of the AIS "Tax-3", as well as subsystems of the AIS "Tax-3", are established by the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
VII. Centralization of tax administration functions within the framework of AIS "Tax-3"
18. The development process of AIS "Tax-3" is aimed at increasing the number of subsystems included in the centralized architecture and correspondingly reducing the number of technological processes automated within the distributed architecture.
19. The transfer of decentralized components of the AIS "Tax-3" into the centralized architecture of application infrastructure components provides high flexibility in scaling the technological resources of the Federal Tax Service of Russia and is based on the following principles:
a) thoughtful and effective division of functions and tasks between promising and legacy components of the system and at all stages of the transition period to ensure efficient and error-free work of personnel;
b) preservation of investments;
c) ensuring the continuity of technological processes;
d) ensuring maximum transparency of the interaction of information system components;
e) ensuring data integrity and consistency.
20. The functions of the centralized and decentralized components of the AIS "Tax-3", which are in commercial operation, are aimed at creating a single information space of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, used to improve the quality of the functions of tax administration and control, and do not overlap.
21. When transferring the decentralized components of the AIS "Tax-3" into the centralized architecture of application infrastructure components, the following approaches are used:
a) use of unified regulatory and reference information;
b) use of unified data identification, in particular the assignment of unique federal identifiers;
c) reconciliation (ensuring data purity) and moving data from decentralized components to centralized ones (to the federal repository);
d) providing the possibility of interaction between subsystems and components of the AIS "Nalog-3" in the process of exchanging and using data to ensure the implementation of continuous technological processes;
f) ensuring a consolidated collection of information security events in end-to-end technological processes.
22. A separate set of processes that are currently already implemented within the framework of an automated information system and are planned for implementation are not subject to centralization due to its impossibility or economic and organizational inefficiency. Such decentralized components, along with components of the centralized environment, support and will continue to support the continuity of execution of technological processes of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
VIII. The procedure for providing access and organizing work with AIS "Nalog-3"
23. Access to the AIS "Tax-3" is provided to system users using specialized access control tools.
24. Registration in the AIS "Tax-3" of users of tax authorities and organizations subordinate to the Federal Tax Service of Russia is carried out in accordance with the procedure for providing access to information systems and resources of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
25. In order to organize work with the AIS "Tax-3", users of the system take organizational and administrative measures, providing for:
24.1*. For external interaction:
_______________
*Numbering corresponds to the original. - Database manufacturer's note.
a) identification of authorized employees of the federal executive body who carry out actions to sign electronic documents using a qualified electronic signature;
b) installing the necessary means of cryptographic information protection on automated workstations of authorized employees and providing them with electronic signature tools;
c) allocation of an email address for processing information notifications sent by the AIS "Tax-3" to the subjects of the system about the direction and receipt of information, as well as other actions carried out by federal executive authorities, and processing of these notifications.
24.2. For tax authorities and organizations subordinate to the Federal Tax Service of Russia:
a) appointment of responsible technologists for the purpose of comprehensive organization of the implementation of technological processes of the Federal Tax Service of Russia and the implementation of internal control of activities on technological processes of the Federal Tax Service of Russia;
b) formation and maintenance of the Register of approved applications for development (modernization) work and support services for the AIS "Tax-3" for the next year;
c) ensuring the protection of information resources and system infrastructure.
26. System users registered in the AIS "Tax-3" receive authorized access to the AIS "Tax-3" to perform functions in accordance with their powers.
27. Identification and authentication of users of tax authorities and organizations subordinate to the Federal Tax Service of Russia in the AIS "Tax-3" is carried out using specialized access control tools.
28. Users registered in the AIS "Tax-3" do not have the right to take actions aimed at disrupting the functioning of the AIS "Tax-3" of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
29. The powers of the owner of the information contained in the AIS "Tax-3" are exercised by the Russian Federation represented by the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
30. Access to information contained in the AIS "Tax-3" is provided for system users in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on information, information technology and information protection.
IX. Legal regime of software and hardware tools of AIS "Tax-3"
31. The property included in the software and hardware of the AIS "Tax-3" and created or acquired at the expense of the federal budget is the property of the Russian Federation.
32. The exclusive right to the application software of the AIS "Tax-3" is acquired by the Russian Federation in accordance with the civil legislation of the Russian Federation.
33. The totality of AIS "Tax-3" software, as well as preparatory (design), technical, accompanying and methodological documentation for such software forms the fund of algorithms and programs of AIS "Tax-3".
The procedure for the formation and maintenance of the fund of algorithms and programs of the AIS "Tax-3" is established by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
X. Technological infrastructure of AIS "Tax-3"
34. The target infrastructure intended for the operation of the AIS "Tax-3" is the Federal Data Center of the Federal Tax Service of Russia in Moscow, as well as the Data Center System of the Ministry of Finance of Russia created within the framework of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 5, 2011 N 995.
35. The created system of Data Processing Centers of the Ministry of Finance of Russia and the federal executive authorities subordinate to it includes the Federal Data Processing Center in Dubna, Moscow Region and Reserve Data Processing Center No. 1 in Gorodets, Nizhny Novgorod Region.
XI. The order of development of AIS "Tax-3"
36. The procedure for organizing work on the development (modernization) of the AIS "Tax-3", including planning work, monitoring its execution, the procedure for putting into effect the results obtained is determined by the Regulations on the organization of work on the development (modernization) of the automated information system of the Federal Tax Service (AIS " Tax-3"), approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
XII. Operating procedure for AIS "Nalog-3"
37. The procedure for operating the AIS "Tax-3" is regulated by a system of specialized regulatory documents that define approaches to ensuring the continuity of the functioning of the automated information system and technical support for its users.
38. Operation of the AIS "Nalog-3" and technical support for its users is carried out by a specialized organization subordinate to the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
Technical support for AIS "Tax-3" users is provided using a centralized technical support website.
Electronic document text
prepared by Kodeks JSC and verified against:
newsletter